Georgia
RECENT ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
GDP grew by 10.1 percent y-o-y in 2022 and growth remained robust in 2023, driven by a rebound in private consumption.
During H1 2023, exports grew by 19.3 percent (yoy) in USD value, mostly driven by re-exports of used cars.
FDI inflows recorded an improvement in H1 2023 with an 11 percent increase compared to the same period in 2022, driven by the financial, energy, and manufacturing sectors.
Inflation has declined sharply, driven by lower commodity prices, particularly for food and fuel, along with a strong Georgian Lari (GEL).
The service sector remains strong thanks to a continued recovery in tourism.
The application for EU candidacy, initiated in 2022, provides opportunities for further income growth while requiring significant reforms.
GEORGIA AND THE EaP
The Eastern Partner countries have been making steady progress in improving the business climate for SMEs. This overview of the Doing Business indicator of the World Bank shows how Georgia has improved over the years, gradually closing the gap with the best performing countries of the world (‘distance to frontier’). Georgia has been the stellar performer, starting off very high at 74.1 percent of distance to frontier in 2010, and standing at 83.7 percent in 2020 (latest data available).
Doing Business – Distance to frontier, EaP
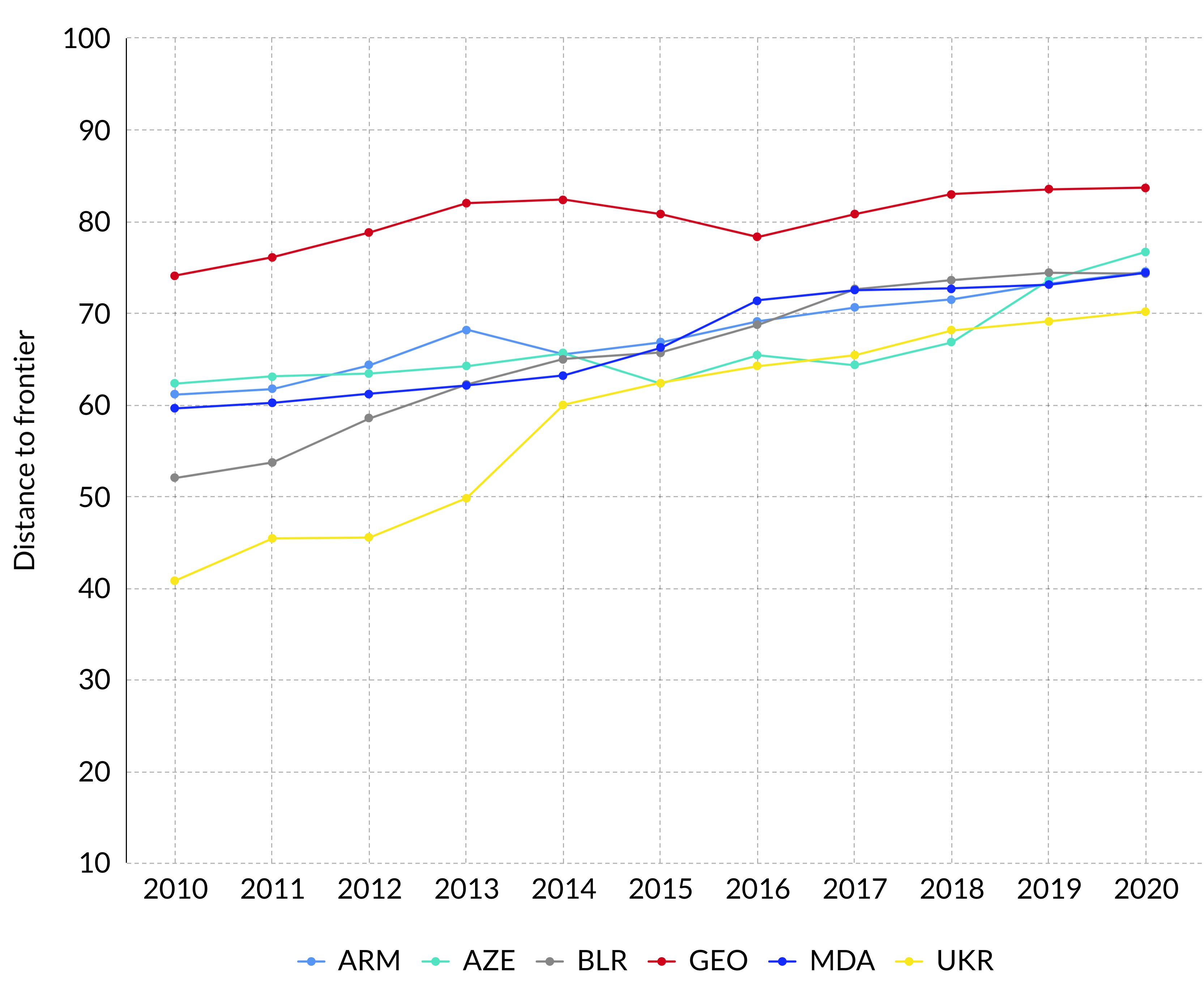
Source: Doing Business, World Bank, www.doingbusiness.org
NATIONAL SME PERFORMANCE
The National Statistics Office of Georgia revised its SME definition in 2017 to comply with EU standards and increase international comparability. Under the recently adopted new definitions and methodology, As of 2020, 99.6 percent of active enterprises in Georgia were SMEs, which accounted for 59.3 percent of business sector employment, 40.8 percent of business sector turnover and 58.0 percent (GEL 25.2 million) of output in the business sector (GEL 43.5 million).
Business demography indicators 2021
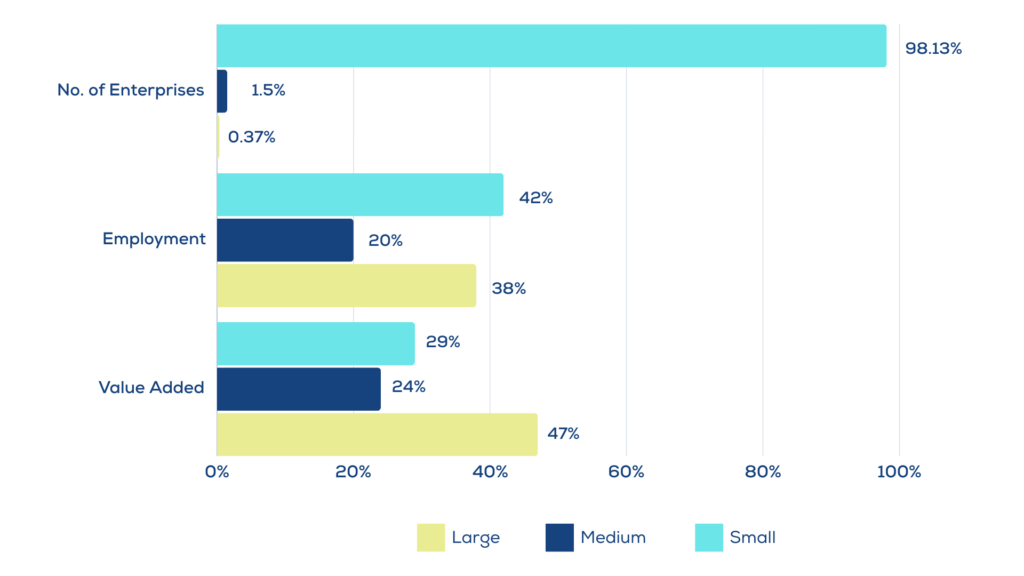
Source: Geostat (2021) and OECD Library.
IMPLEMENTATION PROGRESS
The EU’s support for SMEs in the EaP grew by 1.8 percent in 2021. Results for 2021 show a bounce back in terms of the numbers of SMEs supported by the EU and impressive performance of supported SMEs, creating more income and more jobs than in any previous year. The budget available to support SMEs in Georgia decreased by 8 percent from 2020, from € 300.90 million.
DATA FOR GEORGA IN 2021

